Page 84 - NetWork-En-V3
P. 84
Here are some ways to potentially expand the Wi-Fi range and improve network
coverage:
● Change the placement of the Wireless Access Point to a higher location, free from
obstacles, as signals can propagate better through open spaces. There are
applications like Heatmapper or inSSIDer that can help you choose the best
coverage.
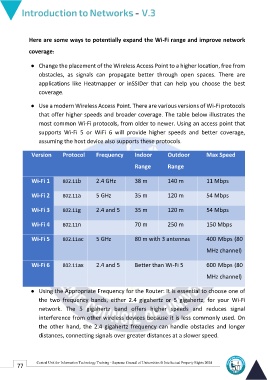
● Use a modern Wireless Access Point. There are various versions of Wi-Fi protocols
that offer higher speeds and broader coverage. The table below illustrates the
most common Wi-Fi protocols, from older to newer. Using an access point that
supports Wi-Fi 5 or WiFi 6 will provide higher speeds and better coverage,
assuming the host device also supports these protocols.
Version Protocol Frequency Indoor Outdoor Max Speed
Range Range
Wi-Fi 1 802.11b 2.4 GHz 38 m 140 m 11 Mbps
Wi-Fi 2 802.11a 5 GHz 35 m 120 m 54 Mbps
Wi-Fi 3 802.11g 2.4 and 5 35 m 120 m 54 Mbps
Wi-Fi 4 802.11n 70 m 250 m 150 Mbps
Wi-Fi 5 802.11ac 5 GHz 80 m with 3 antennas 400 Mbps (80
MHz channel)
Wi-Fi 6 802.11ax 2.4 and 5 Better than Wi-Fi 5 600 Mbps (80
MHz channel)
● Using the Appropriate Frequency for the Router: It is essential to choose one of
the two frequency bands, either 2.4 gigahertz or 5 gigahertz, for your Wi-Fi
network. The 5 gigahertz band offers higher speeds and reduces signal
interference from other wireless devices because it is less commonly used. On
the other hand, the 2.4 gigahertz frequency can handle obstacles and longer
distances, connecting signals over greater distances at a slower speed.
77 Central Unit for Information Technology Training - Supreme Council of Universities © Intellectual Property Rights 2024